主要探究一下malloc和free是如何执行的
!!!说明:本文是杂文,可能只有我能看懂,仅供复习参考使用,不定期更新
malloc
真正发挥作用的是_int_malloc
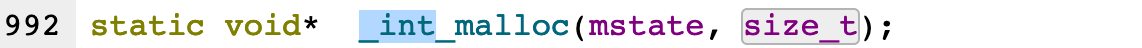
但是call malloc是__libc_malloc

在__libc_malloc中会调用_int_malloc
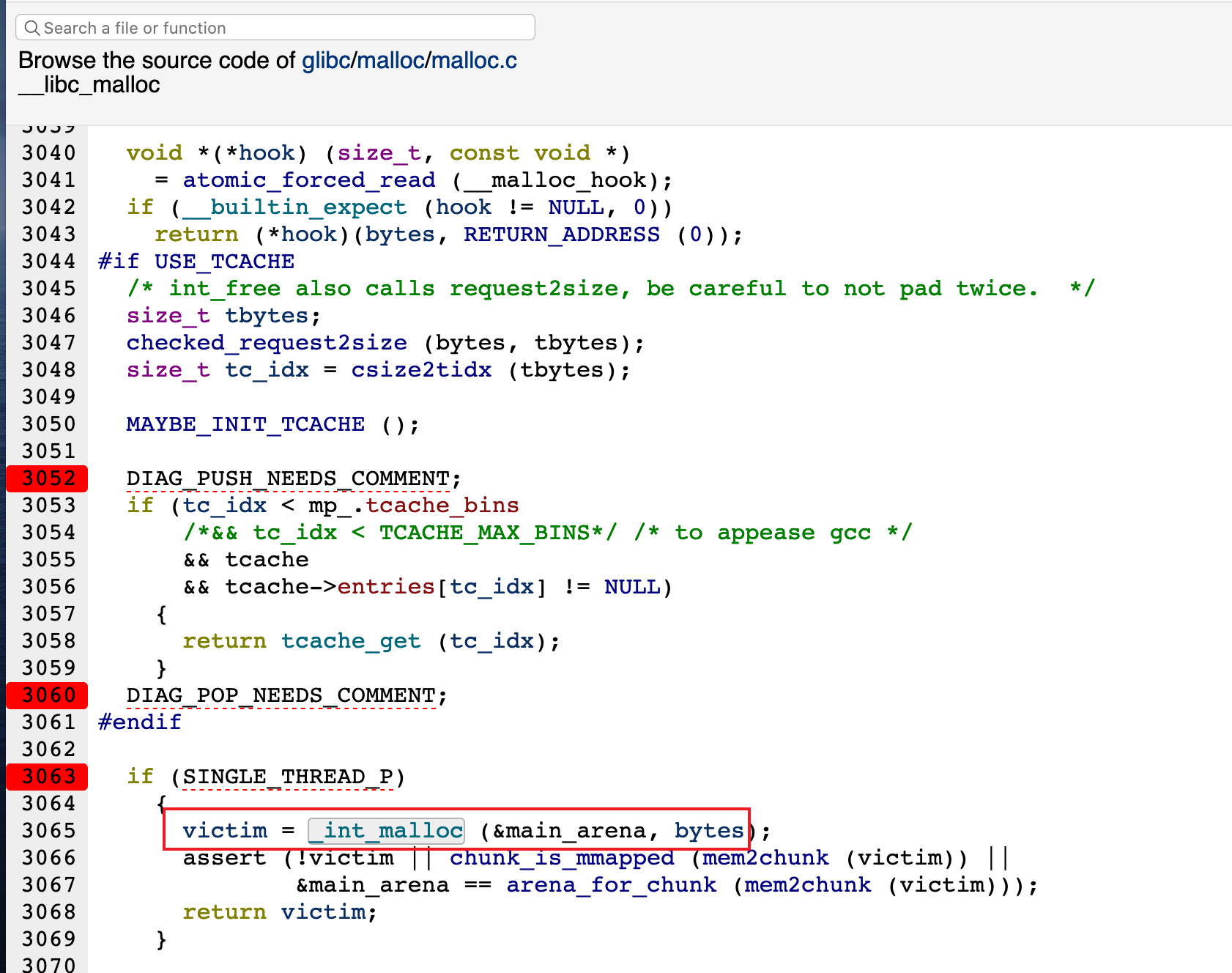
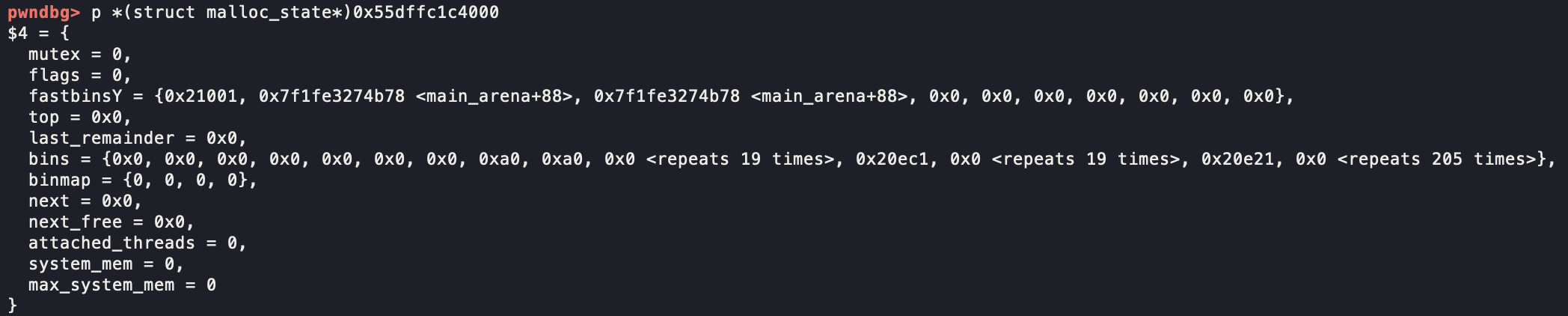
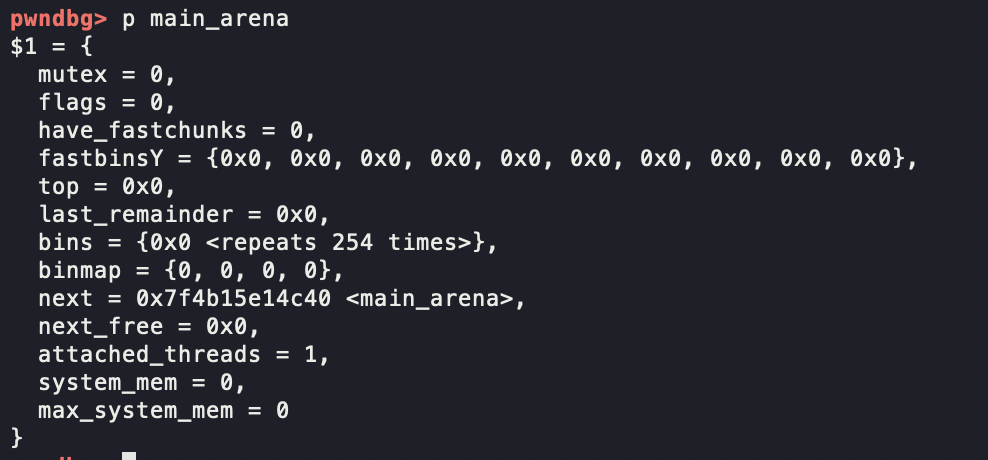
整个heap的信息都记录在struct malloc_state中,称为main_arena
__libc_malloc主体部分如下
hook取得__malloc_hook部分内容
如果指针hook != 0 就调用hook函数
(第一次调用malloc时,__malloc_hook里面其实是有一个叫malloc_hook_ini的函数,该函数首先把__mallochook置0防止再次调用(因为返回地址是__libc_malloc,然后调用了ptmalloc_init()这个做初始化工作的主体函数)
void *
__libc_malloc (size_t bytes)
{
mstate ar_ptr;
void *victim;
void *(*hook) (size_t, const void *)
= atomic_forced_read (__malloc_hook);
if (__builtin_expect (hook != NULL, 0))
return (*hook)(bytes, RETURN_ADDRESS (0));
arena_get (ar_ptr, bytes);
victim = _int_malloc (ar_ptr, bytes);
/* Retry with another arena only if we were able to find a usable arena
before. */
if (!victim && ar_ptr != NULL)
{
LIBC_PROBE (memory_malloc_retry, 1, bytes);
ar_ptr = arena_get_retry (ar_ptr, bytes);
victim = _int_malloc (ar_ptr, bytes);
}
if (ar_ptr != NULL)
__libc_lock_unlock (ar_ptr->mutex);
assert (!victim || chunk_is_mmapped (mem2chunk (victim)) ||
ar_ptr == arena_for_chunk (mem2chunk (victim)));
return victim;
}
点进去arena_get
/* arena_get() acquires an arena and locks the corresponding mutex.
First, try the one last locked successfully by this thread. (This
is the common case and handled with a macro for speed.) Then, loop
once over the circularly linked list of arenas. If no arena is
readily available, create a new one. In this latter case, `size'
is just a hint as to how much memory will be required immediately
in the new arena. */
#define arena_get(ptr, size) do { \
ptr = thread_arena; \
arena_lock (ptr, size); \
} while (0)
我们直接上手跟踪好了
#Include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
void *p,*q;
p = malloc(100);
q = malloc(16);
return 0;
}
可以看到,第一次调用malloc时,会进去malloc_hook_ini函数
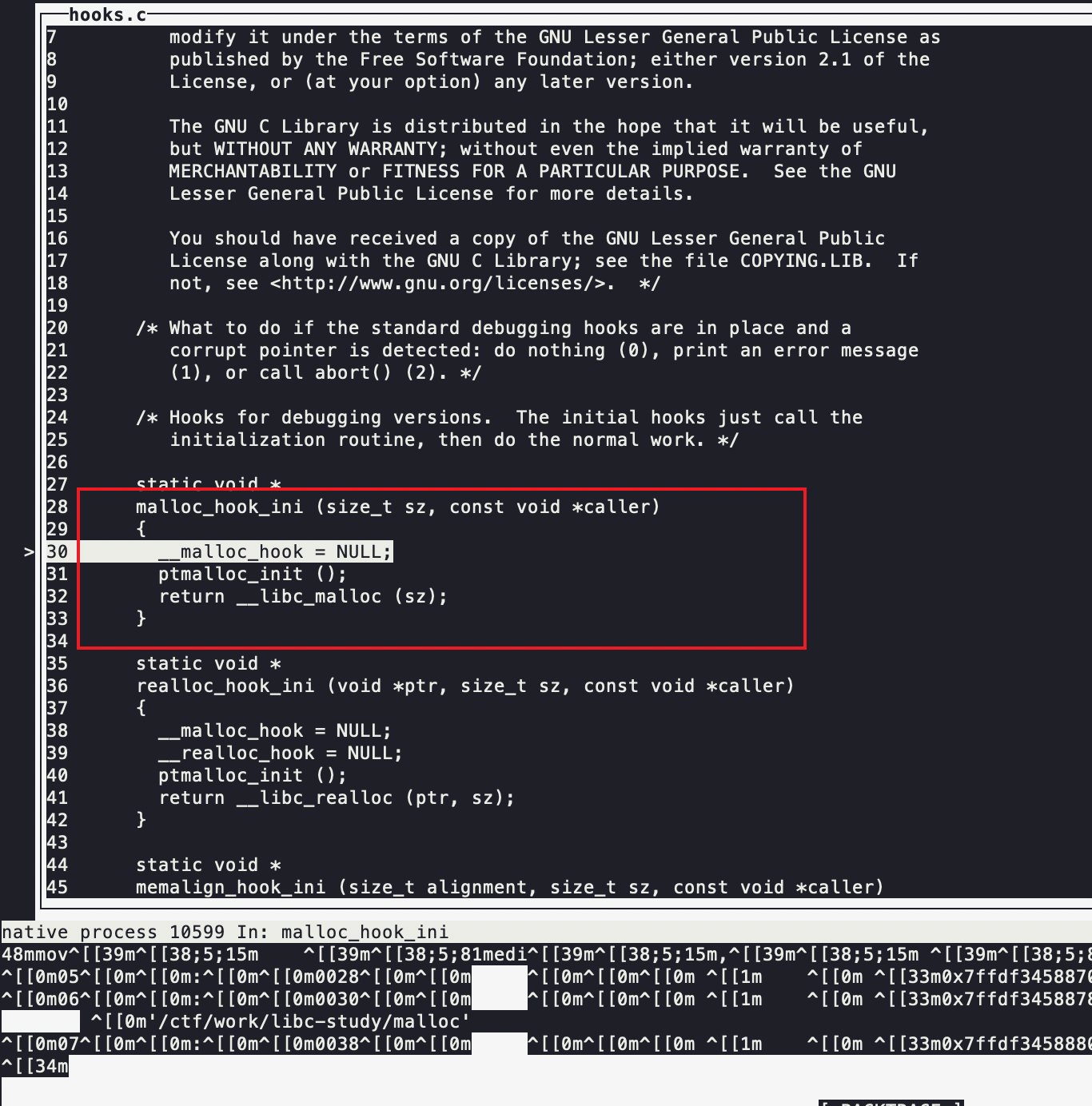
执行完后返回到__libc_malloc函数里面
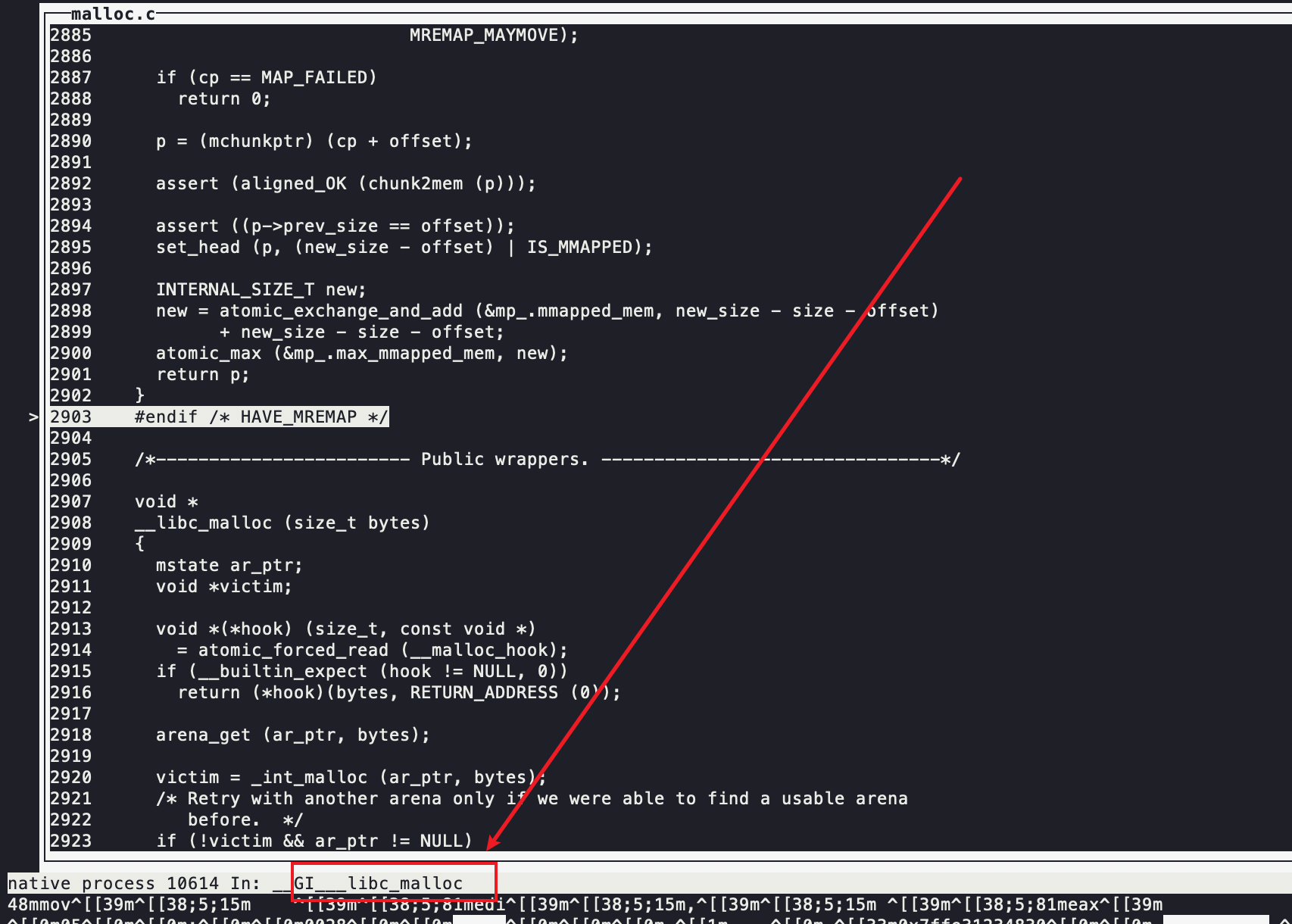
free
我们通过这个demo看一下free过程中发生了啥
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
void *p,*q,*r;
p = malloc(150);
q = malloc(150);
r = malloc(150);
free(p);
free(r);
free(q);
}
如图,我们现在申请了三个chunk
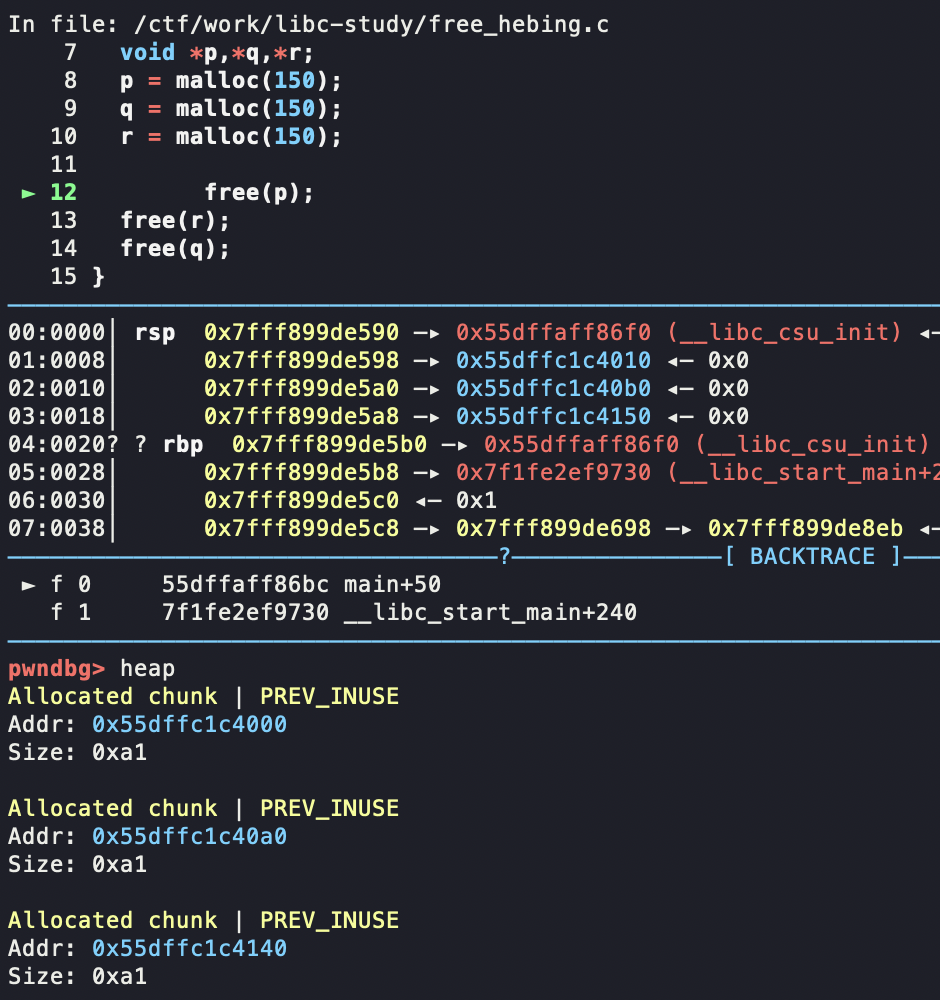
free掉一块,可以看到进入unsorted bin中去
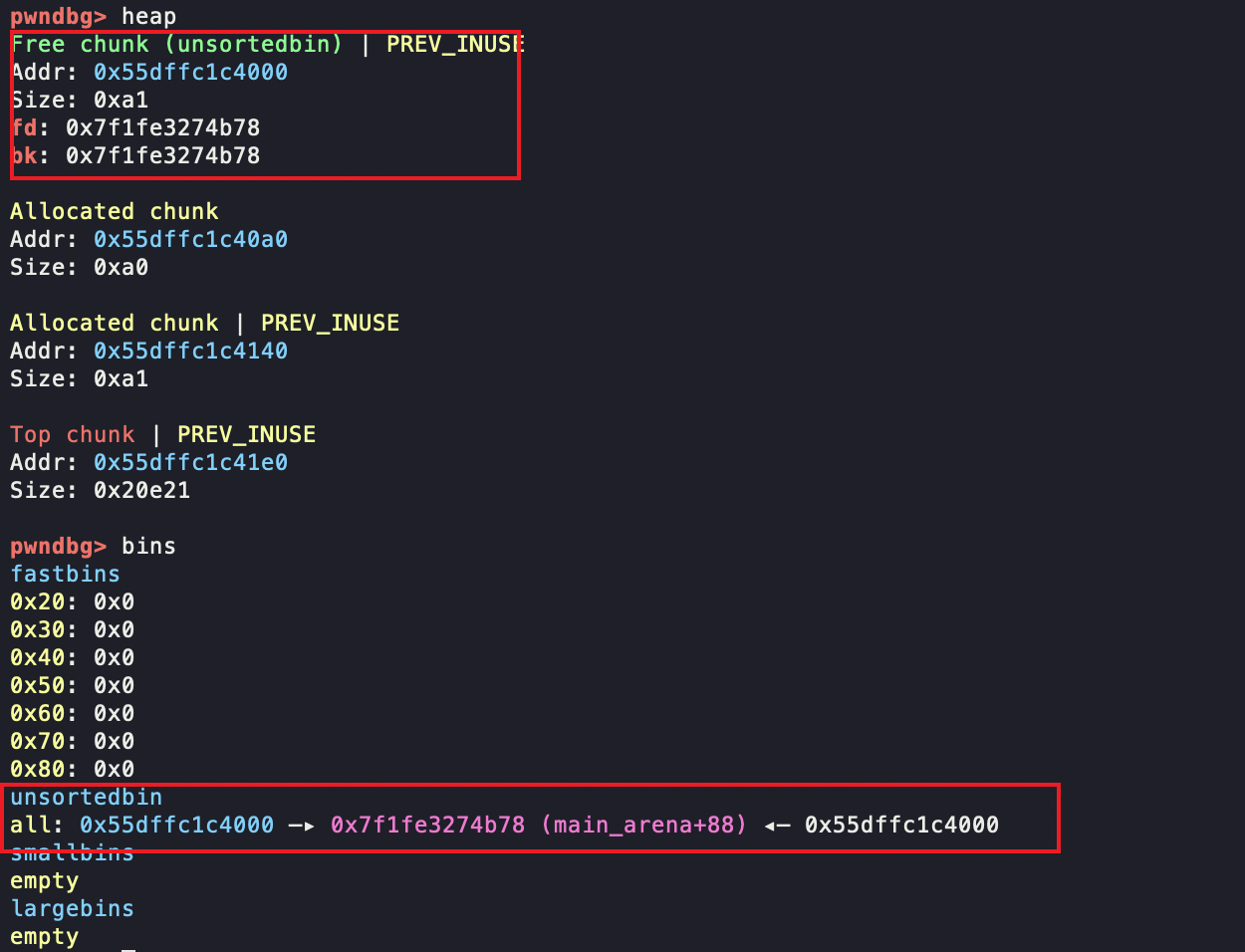
把r free掉,可以看到直接和top chunk合并了
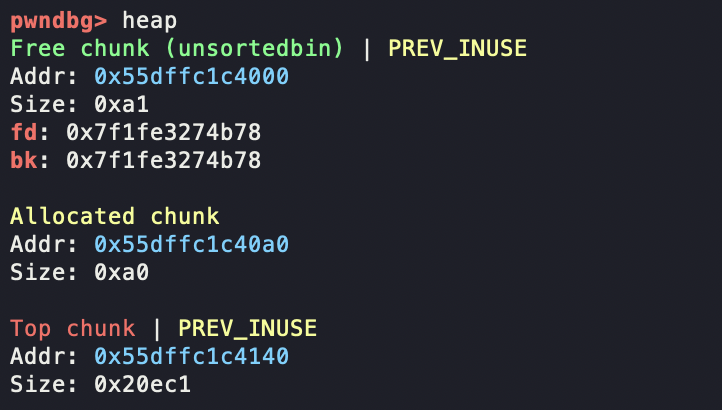
思考:如果free q后,是q先和p合并呢还是先和topchunk合并呢??
调试小技巧

可以看到,其实是先和前一块chunk进行合并的
size加上prevsize之类的
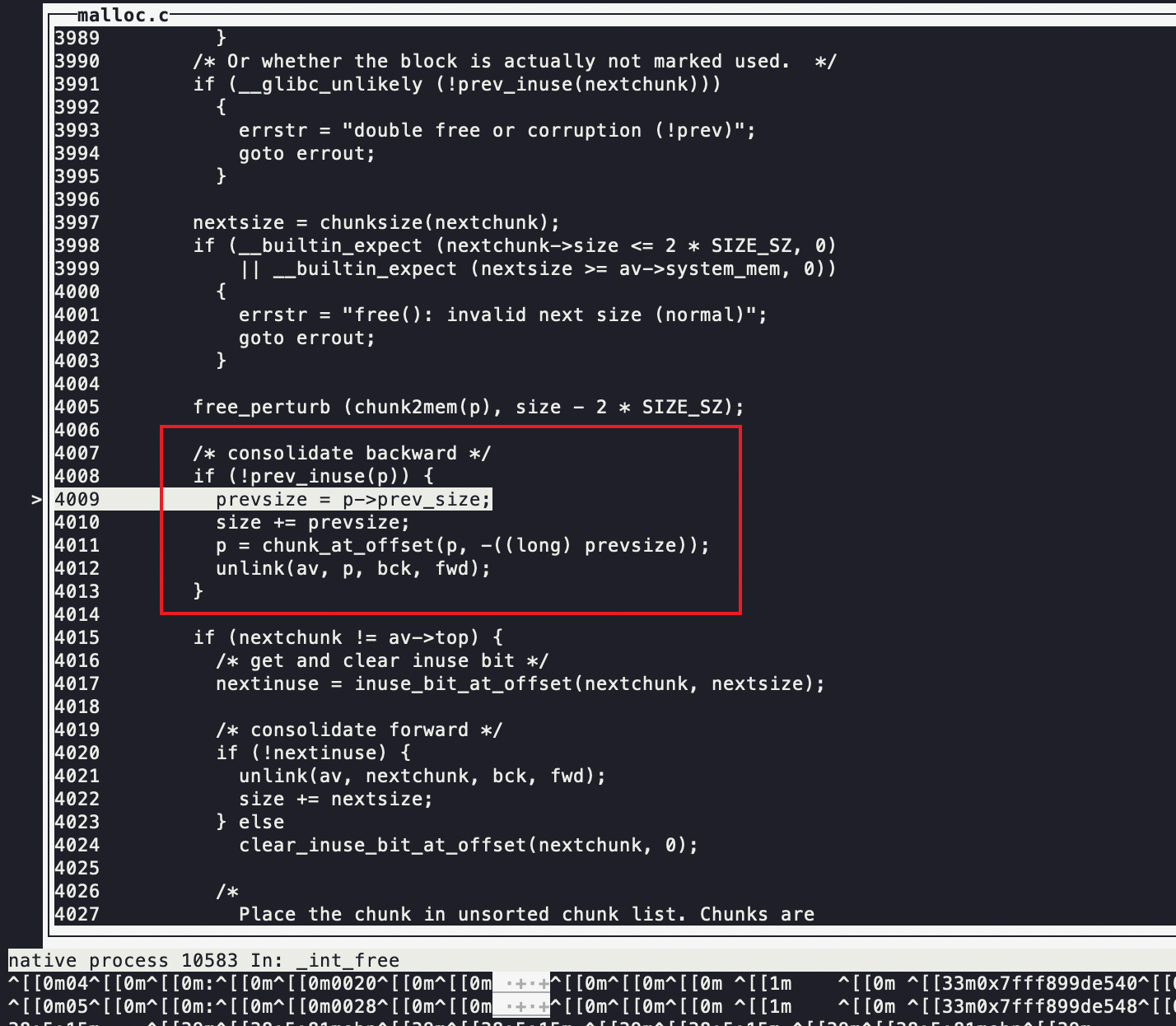
小技巧,p *(struct malloc_state*)address可以将某个地址的堆块详细信息打印出来
可以看到,最终三个chunk都被top chunk合并起来